
본 포스팅은 성균관대학교 최재영 교수님의 '컴퓨터 비전(Computer Vision)' 강의 내용을 참고하여 작성되었습니다.
컴퓨터 비전 :: Geometric Camera Models
Image Formation의 Factors
- Geometry(위치 관계)
- Radiometry(복사량, 색상, 반사된 빛의 양)
- Photometry(빛의 세기)
- Digitizaion(연속적 → 이산적으로 변환)
Image Transformation
· 선형 변환
- 선형 변환의 경우 P'=T(p)에 따라 아래와 같이 표현 가능
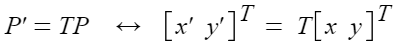
(1) 크기 변환(Scaling)

(2) 반전(Mirroring)
① y축에 대한 반전

② y=x에 대한 반전

(3) 각도(θ) 변환(Rotation)
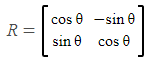
- 아래와 같은 좌표의 평행이동(2D Translation)은 Linear하지 않다

이를 Linear하게 표현하려면?
→ 동차좌표(Homogeneous Coordinates) 활용 (행렬의 덧셈이 아닌 곱의 형태로 변환)
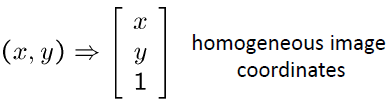
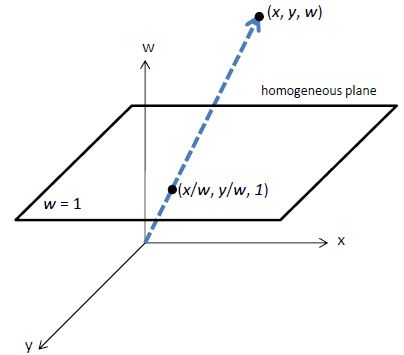
*Converting From Homogeneous Coordinates
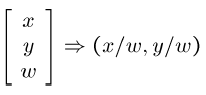
· Image Transform의 4가지 형태
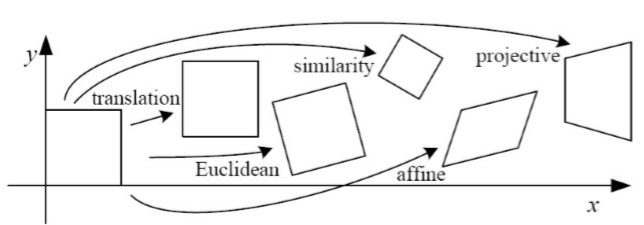
(1)-1 Rigid Transformation (강체 변환) : Translation
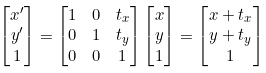
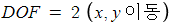
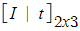
(1)-2 Rigid Transformation (강체 변환) : Euclidean
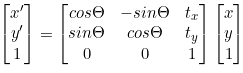


(2) Similarity Transformation(동질 변환)
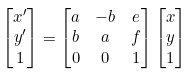
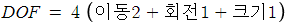
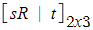
(3) Affine Transformation(형태 변환) - 선형성 추가(직선의 평행관계 보존)

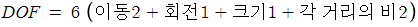

(4) Perspective Transformation(원근 변환) - Projective, Homography

*Perspective properties
Origin (X), Line (O), Parallel (X), Ratio(X), 곱의 형태(O)

Geometric Camera Models
· Two Coordinate Sys
① 카메라의 좌표
② 실세계(Real World)의 좌표
· Pinhole camera model

① 핀홀 크기의 영향
· 핀홀 크기가 크면 빛이 혼합되어 Blurred
· 핀홀 크기가 작으면 빛의 양이 적어져서 Dark, 회절(Diffraction) 발생 → 촬영시간을 길게
② 렌즈의 사용
· 필름에 Focus할 경우 회절로 인해 초점이 맞지 않는 현상이 발생(Circle of Confusion)
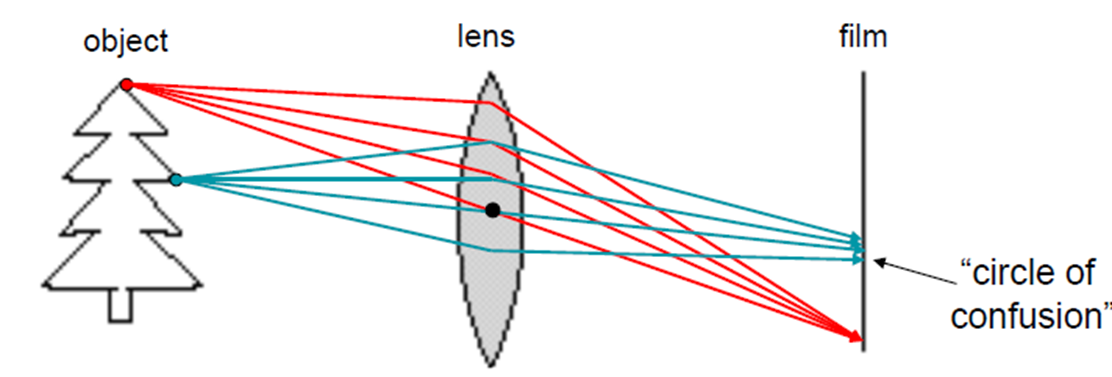
· Focal point를 활용하여 필름에 object를 투영한다.
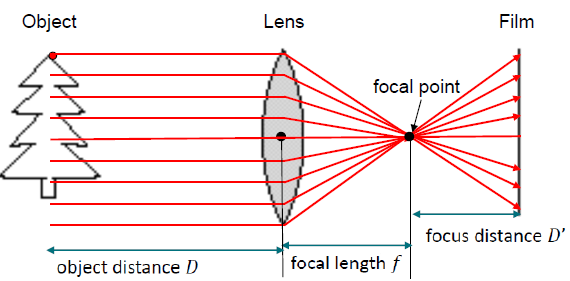
· Thin Lens Formula
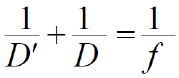
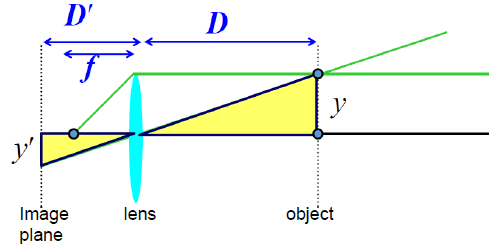
- 식 유도

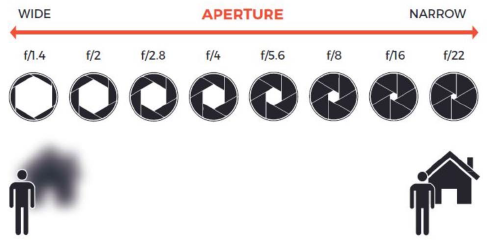
· Depth of Field
- Depth of Field : 초점이 잘 맞는 구간
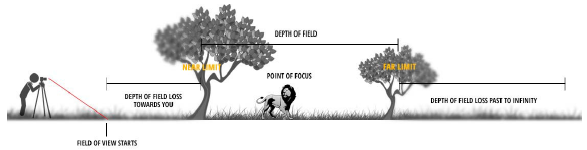
Wide(ex. f/1.4) aperture → Small DoF
narrow(ex. f/22) aperture → Large DoF
· Field of View (시야각)
- focal length(f)가 길어질 수록 시야각(φ)는 좁아진다.
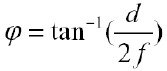
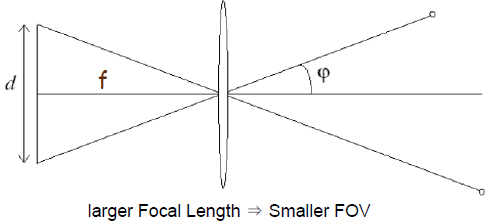
· Relationship between Pinhole Camera Model and coordination
(1) Intrinsic Camera Coordinate
- 아래 Pinhole camera의 camera matrix P를 구해보자 (p의 shape은 3x4)

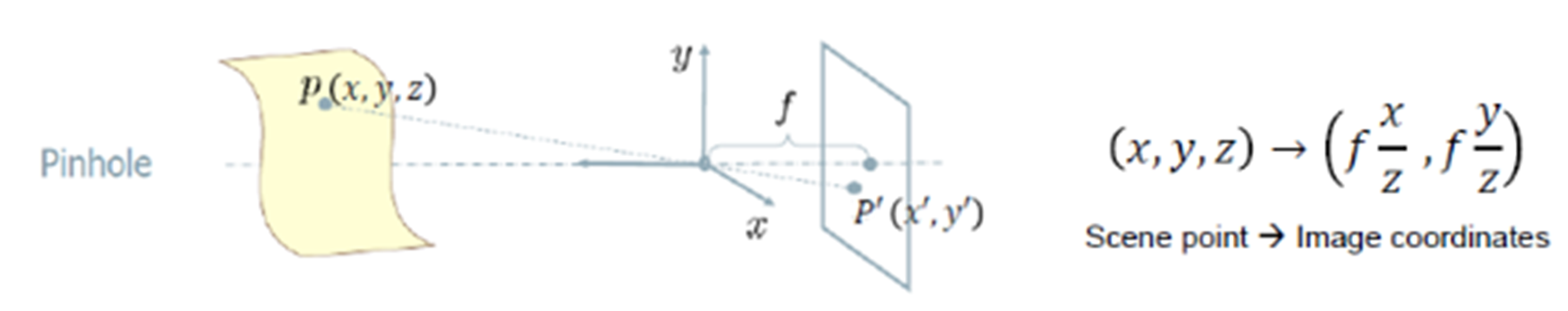
- 카메라와 이미지의 좌표값 차이 보정
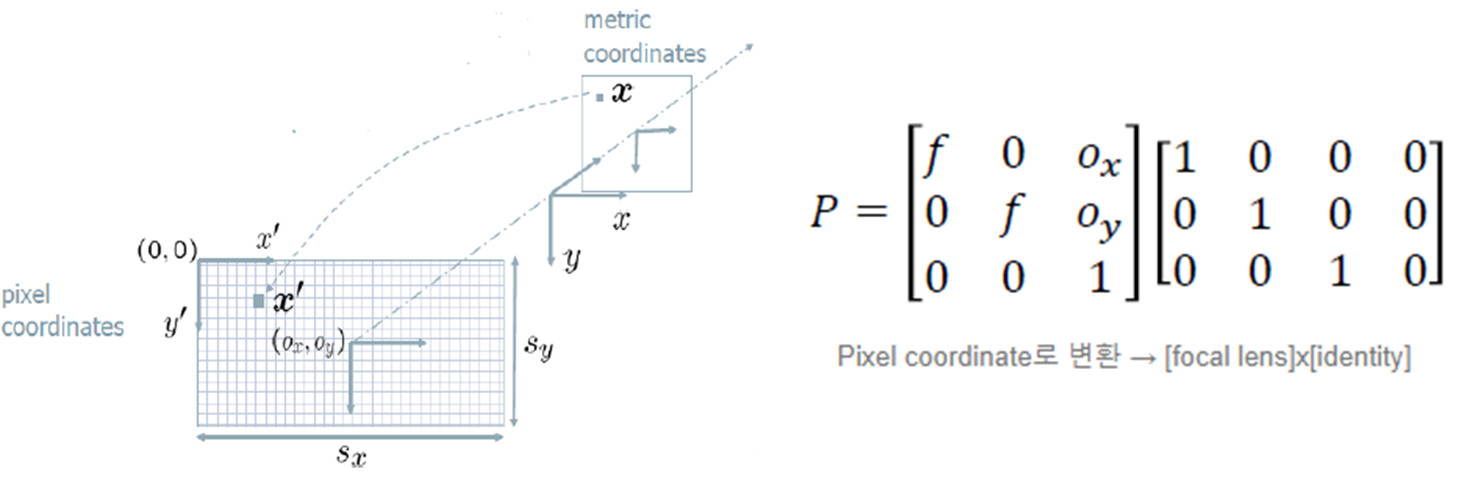
(2) Extrinsic Camera Coordinate
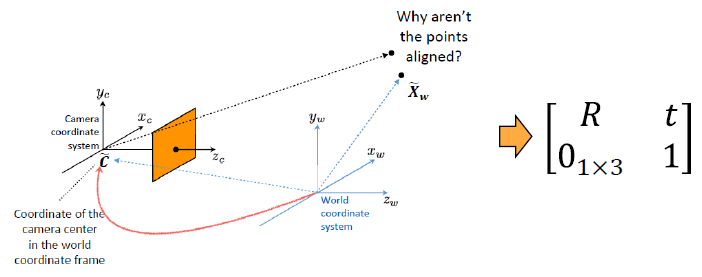
(3) Complete Camera Model
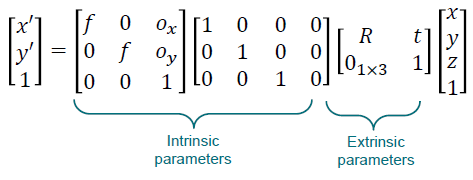
(4) General Camera Model
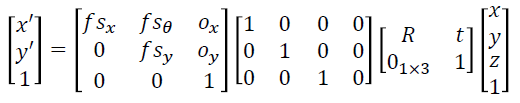
'DataScience > 컴퓨터비전' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Feature Matching (0) | 2023.06.19 |
|---|---|
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Feature Descriptors (1) | 2023.06.18 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Local Feature Detection (1) | 2023.06.17 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Image Pyramids (0) | 2023.06.16 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Linear Filters(Cross-correlation, Convolution) (0) | 2023.06.15 |




댓글