
본 포스팅은 성균관대학교 최재영 교수님의 '컴퓨터 비전(Computer Vision)' 강의 내용을 참고하여 작성되었습니다.
컴퓨터 비전 :: Feature Matching
Fitting, Alignment, RANSAC
· Fitting
- Condition : Input은 Noise(Clutter, Outliers, Multiple lines, Occlusion)를 포함한 point들의 집합
- 점들이 Line을 따라 위치할 때 최적의 라인을 찾는 법 → Least squares
- Outlier가 있다면? → Robust fitting, RANSAC
- Line이 많을 경우? → Voting methods, RANSAC, Hough transform
- Line인지 확실치 않다면? → Model selection
· 일반적인 최소제곱법(Least squares line fitting)

- 위의 최소제곱법을 사용시, 수직성분만 고려하여 Rotation에 Not Invariant하다. 만약 x=a와 같이 x축에 수직인 라인의 경우 구할 방법이 없다.
· Total least squares

- Least squares method는 Outlier에 Weak하다.
→ M-estimation(M-e), Least median of square(LMS) → Outlier에 강인한 알고리즘
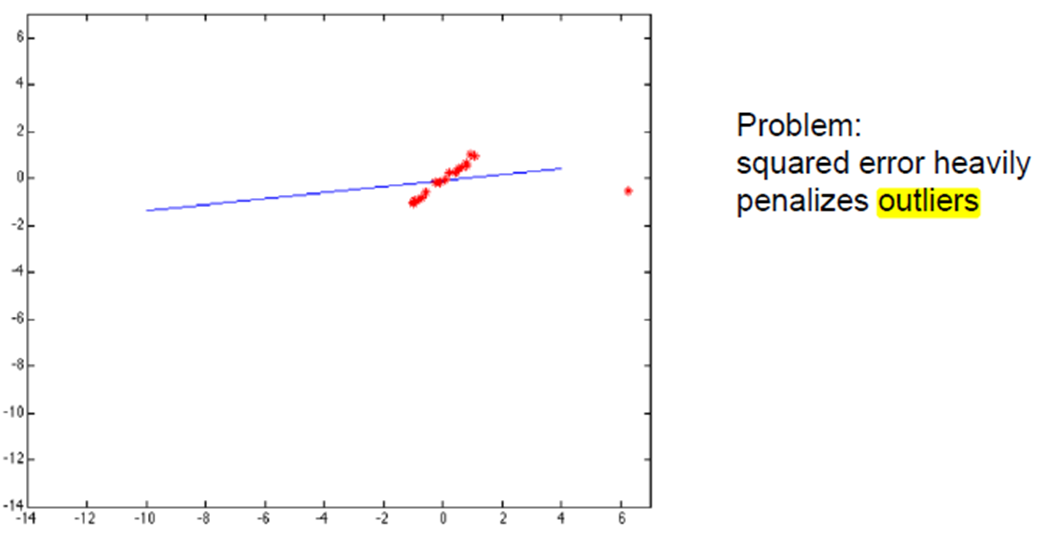
RANSAC(RANdom SAmple Consensus) - Outlier에 매우 Robust
· RANSAC 수행 순서
① 임의의 Data sample을 뽑고
② fitting(=hypothesize a model) 후
③ 각 점과의 거리로 fitting line과 error function을 계산한다. 단, fitting line에서 어느 정도 거리와의 값은 Outlier 처리하여 무시한다.
④ threshold 내의 data 갯수를 센다.
⑤ 이를 반복하고 가장 최소 거리를 선택 후 모든 lnlier로 refit(재 피팅)
· 파라미터 선택
- Initial number of points : S
- 거리 임계값(Threshold) : t
: inlier의 확률(p)로 계산
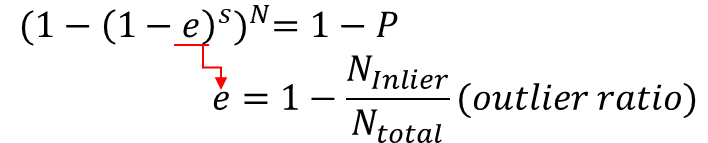
- 샘플의 수 : N

"Outlier 비율이 작을 수록 적은 샘플 횟수 N으로 찾는다."
- 장점 : 간단하고 일반적으로 사용되며, 성능이 좋다.
- 단점 : 많은 변수 튜닝이 필요하다(Initial point, threshold, number of sampling, set of inlier)
Outlier ratio가 높을 수록 성능이 저하된다.
· Another Feature Matching
1) Brute-Force Matcher
: Feature를 하나 찾고 비교 대상에서 모든 Feature와 일일이 비교하는 방식
→ 차잇값의 최솟값을 가진 거리를 찾음(Least square)
2) FLANN Matcher (Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbor)
: Dictionay 자료형 사용{"descriptor index" : "descriptor 계수", ...}, 각 descriptor를 비교해가며 최솟값을 찾음
· Correspondence(일관성)
- 특징찾기 → 같은 것을 매칭 → Outlier는 제거 → 남은 특징들에 대한 변환식 T 파악 → 나머지 점들을 변환(Image Alignment)
- Image alignment 접근법
(1) Direct(pixel-based) alignment
(2) Feature-based alignment
ex) affine transform - DOF 6

- Image translation만 사용시 alignment가 아래와 같이 맞지 않는 경우가 발생한다. → Image Homography 사용

· Homography, Rectification, Stitching
- Homography : plane projective(=perspective) transformation, Image Warping

- Homogeneous 좌표를 사용
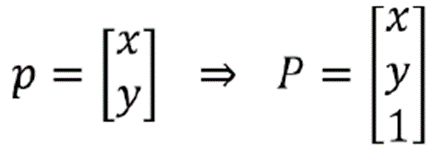
- Homography matrix를 곱해준다.
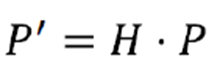
- 아래의 식에 의해 heterogeneous 좌표로 변환이 가능하다.
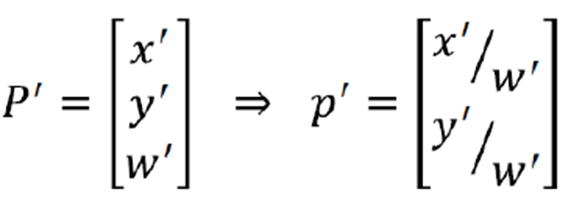
- Linear equation for each correspondence(3×3)
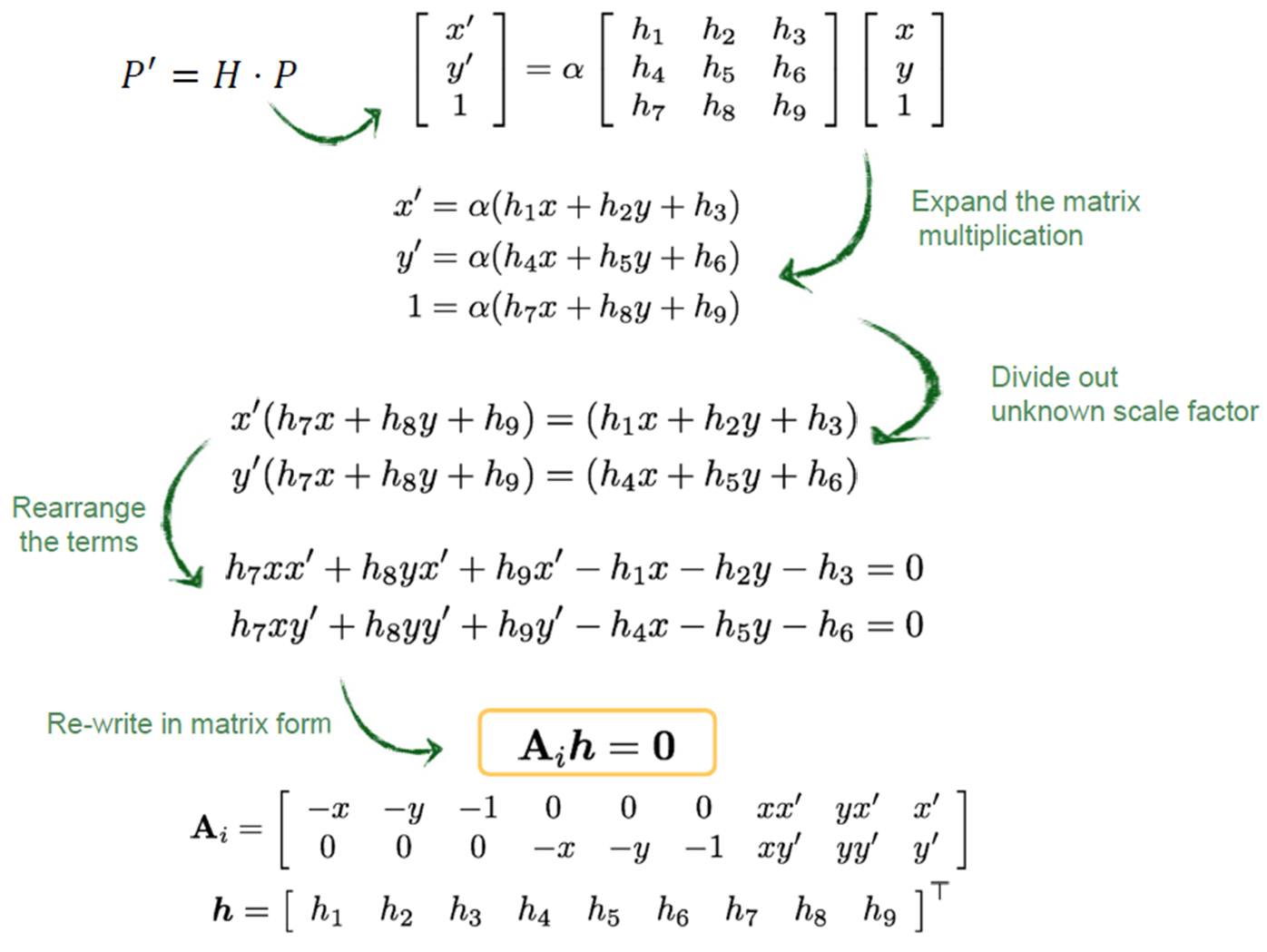
· Homogeneous linear least squares problem(LLS)
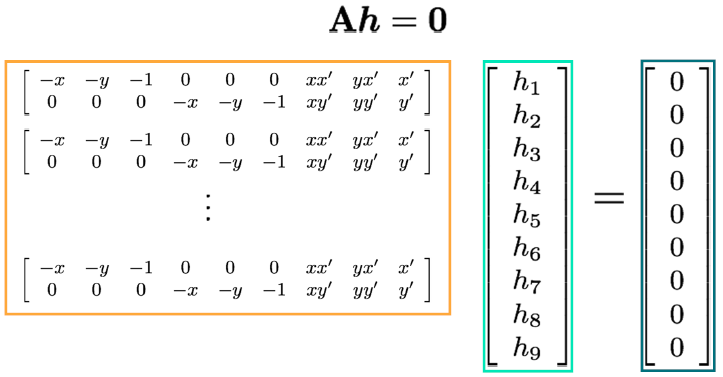
· SVD(Singular value decomposition)
- Eigen value 구하기
: AA^T : det(AA^T) → 특이값 → u_i 시리즈 구하기
→ Spectral Decomposit :

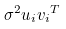
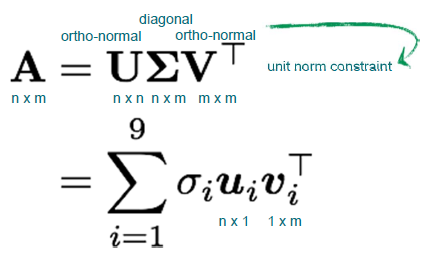
· RANSAC Loop
(1) 포인트 선택(Randomly, inlier에 해당되는)
(2) H 계산(Homography matrix)
(3) Inlier 갯수 확인
(4) 가장 많은 inlier수일 경우 H 기록
→ Recompute H using all inlier
- 매칭 검사

· Removing Seams : 이미지를 붙일 때 나타나는 Seams 제거

- 카메라에 들어오는 빛의 양 차이로 발생 → Vignetting
① multi-band Blending으로 해결
: Image pyramid를 이용한 multi-resolution, seam은 제거하고 sharp detail은 보존

② Feathering : 그라데이션으로 각 이미지가 어두워짐

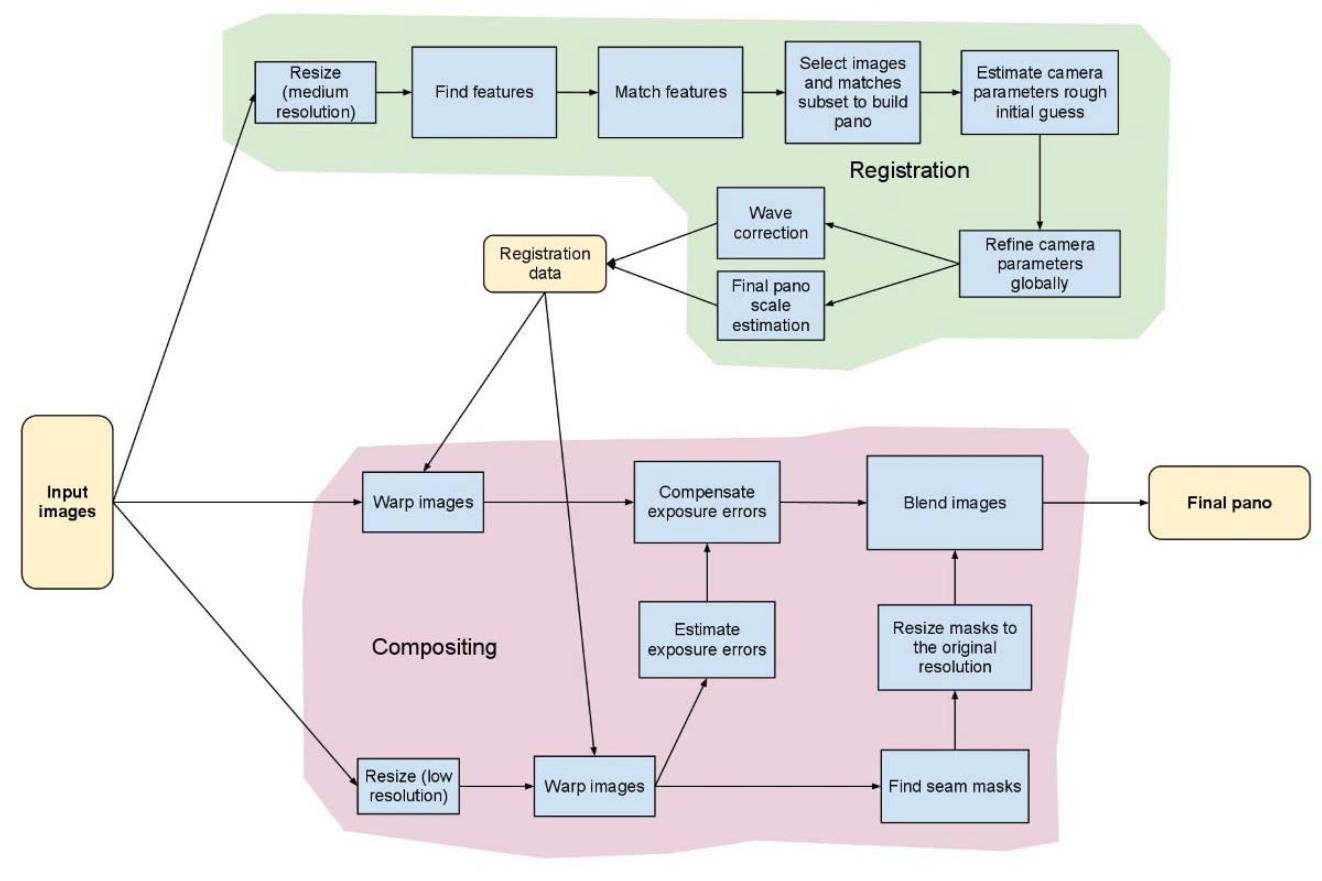
· Stitching pipeline in openCV
'DataScience > 컴퓨터비전' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Stereo Vision (0) | 2023.06.20 |
|---|---|
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Feature Descriptors (1) | 2023.06.18 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Local Feature Detection (1) | 2023.06.17 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Image Pyramids (0) | 2023.06.16 |
| 컴퓨터 비전 :: Linear Filters(Cross-correlation, Convolution) (0) | 2023.06.15 |




댓글